
How to Start Nixcoders.org Blog: A Simple Guide for Everyone
Introduction: What Is Nixcoders.org and Why Start a Blog? Starting a blog is like building your own tiny space on…

Online Tool Guide ZardGadjets: Master Your Workflow Like a Pro
“Online Tool Guide ZardGadjets” In a world overflowing with digital tools, finding the right one can feel like looking for…

Renovate or Extend? How to Choose the Right Path for Your Home
When it comes to making your home truly your own, the decision to renovate or extend can feel overwhelming. However,…

Intratone – Why Go Wireless?
Wireless intercom and access solutions provide a significant leap forward in both capability and convenience. Key benefits include: Whether you’re…

Innovation News Dualmedia: A Bright Spotlight on New Ideas
Introduction Innovation News Dualmedia is a special kind of news that shares fresh, exciting ideas using both words and visuals…

Green Escapes in the City: How Artificial Turf is Revitalizing Urban Spaces
With the rapid growth of urbanization, cities are continuously evolving, often at the expense of natural green spaces. As buildings…
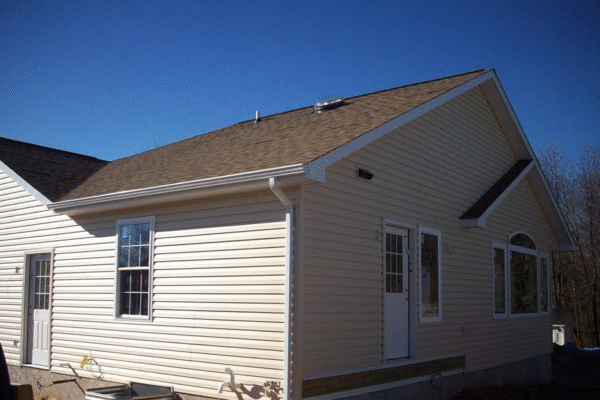
Storm-Ready Roofing: Resilient Solutions for Tampa’s Extreme Weather Challenges
As extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and tornadoes, become more frequent, homeowners are increasingly prioritizing resilient roofing solutions. In…

All About aviyne .com
Introduction aviyne .com is like a special place on the internet built to help people with their daily tasks. Whether…
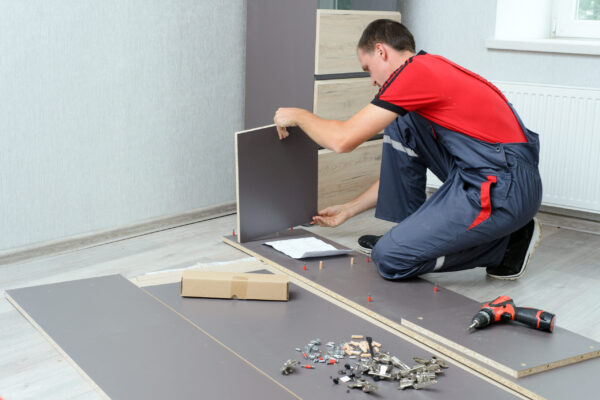

From Delivery to Design: A Step-by-Step Guide to Professional Furniture Installation
When it comes to furnishing your home or office, the process involves more than choosing the right pieces. Professional furniture…

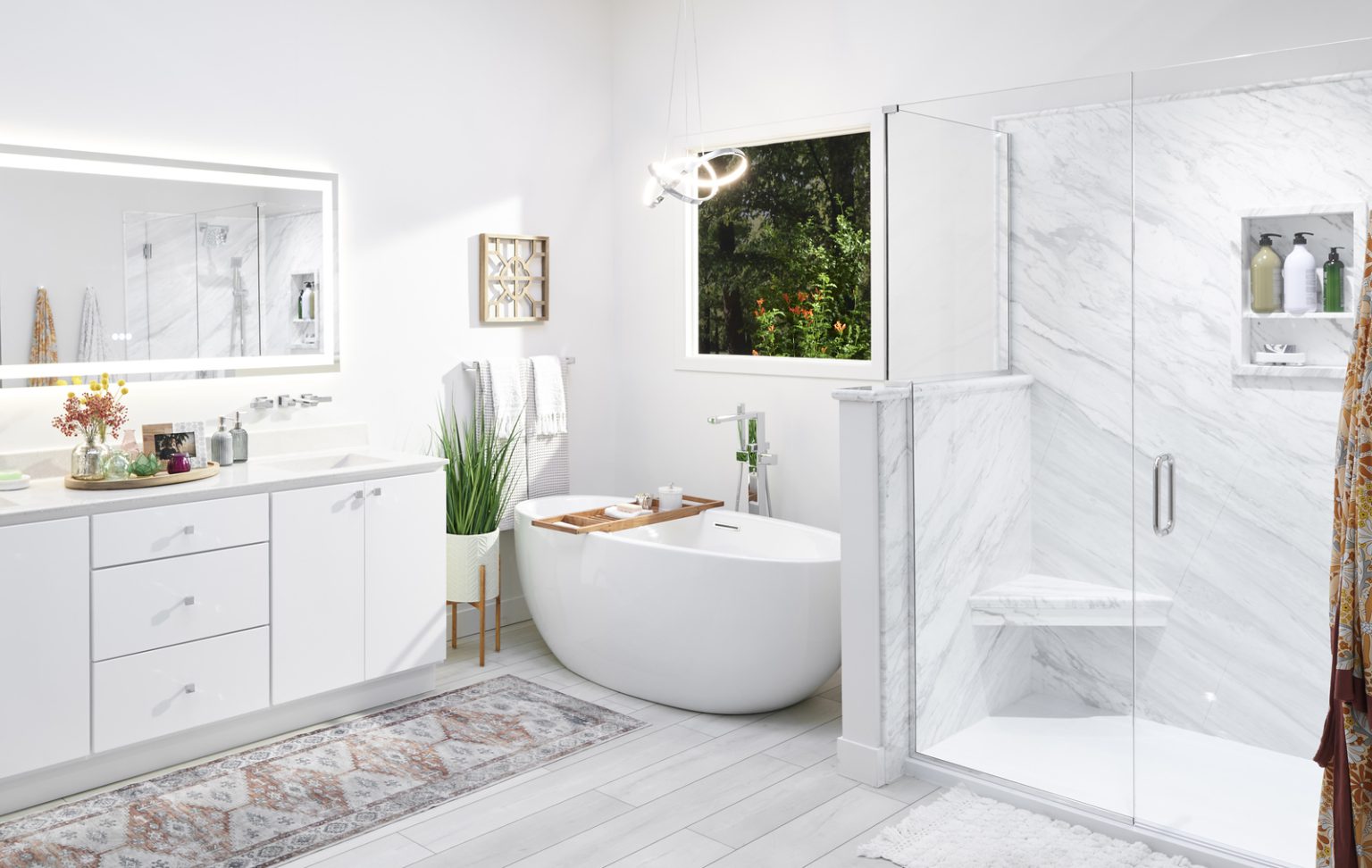
Transform Your Space: Top Flooring Choices for a Stunning Bathroom Remodel in Tampa
When considering a bathroom remodel, one of your primary choices is selecting the best flooring. The bathroom is a high-traffic,…




















I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!